Summary:
- The Federal Reserve held interest rates steady and gave no signal of a September cut.
- Developers and brokers are calling for lower borrowing costs to unlock supply and revive stalled deals.
- The Fed’s decision followed surprise news that the U.S. economy grew 3 percent in Q2.
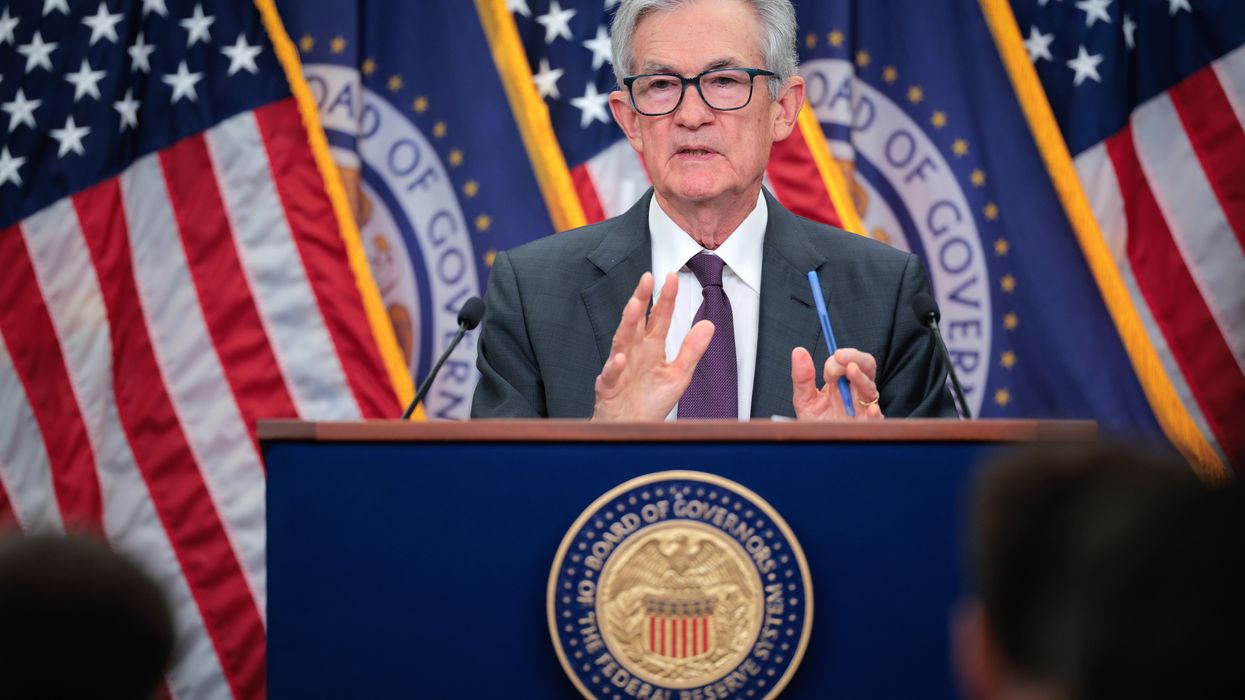
THE FEDERAL RESERVE held its key interest rate steady and gave no indication of a cut in September, despite growing pressure from President Trump and his Fed appointees, USA Today reported. The July 30 decision keeps the Fed’s benchmark rate at 4.25 percent to 4.5 percent for a fifth straight meeting.
The Fed remains caught between its mandates of maximum employment and stable prices, the newspaper said. A slowing job market supports rate cuts, but rising inflation from Trump’s tariffs has made officials cautious about signaling next steps.
“Uncertainty about the economic outlook remains elevated. The Committee is attentive to the risks to both sides of its dual mandate,” the Fed said. “In considering the extent and timing of additional adjustments to the target range for the federal funds rate, the Committee will carefully assess incoming data, the evolving outlook, and the balance of risks.”
The Fed said it considers labor market conditions, inflation pressures and expectations and financial and international developments in making its decisions.
Republican Fed governors Christopher Waller and Michelle Bowman dissented, favoring a rate cut, the first double-governor dissent since 1993. Waller has said tariff-driven inflation will likely be temporary and ease next year. Both are seen as potential Trump picks to succeed Powell when his term ends in May.
In its statement, the Fed dropped its earlier claim that uncertainty had diminished. That more optimistic tone had followed Trump’s 90-day pause on many tariffs, but a Friday deadline could reinstate the higher levies.
The Fed also said “economic activity moderated in the first half of the year”—a downgrade from its earlier description of growth as “solid” that could open the door to a September cut.
“We have made no decision about September,” said Jerome Powell, Fed’s chair, according to USA Today.
He said that the Fed hasn’t cut rates this year because the 4.1 percent unemployment rate meets its full employment goal, while its preferred inflation measure is 2.7 percent—above the 2 percent target. The Fed cuts rates to support growth and jobs and keeps them high to curb inflation.
“When we have risks to both goals, one is farther from target—and that’s inflation,” Powell said. “That calls for a modestly restrictive stance right now.”
In real estate, there’s broad agreement that rate relief is urgent, Real Deal reported. The pressure is acute in housing.
On CNBC Wednesday, LeFrak Organization’s Richard LeFrak compared housing costs to gas prices, something Americans feel immediately, and called for cuts to ease pressure on builders and buyers.
“It would be helpful to increase the supply of housing for interest rates to go down,” he said, framing the crunch as rate-driven as much as policy-driven.
This year’s spring sales season was the slowest in 13 years, according to Bloomberg, with mortgage rates stuck near 7 percent and affordability near its worst since the 1980s. Some buyers are backing out entirely.
Developers and brokers nationwide are increasingly vocal in calling for lower borrowing costs to unlock supply and restart stalled transactions. LeFrak, active in luxury and multifamily development, said rate-sensitive projects remain on hold.
“Do I think rates should be lower? Yes,” he said.
Fanning the flames, the Fed’s decision also came just after the surprise news that the U.S. economy grew at a 3 percent annual pace in the second quarter, topping the Dow Jones estimate of 2.3 percent.
“2Q GDP JUST OUT: 3%, WAY BETTER THAN EXPECTED! ‘Too Late’ MUST NOW LOWER THE RATE. No Inflation! Let people buy, and refinance, their homes!” President Trump posted on Truth Social Wednesday morning.
Still, Powell and his colleagues are wary of easing too soon.
Forbes reported that mortgage rates peaked at 7.04 percent in January, fell to the mid-6 percent range in March, and held between 6.75 and 6.9 percent since May, ending June at 6.77 percent.